
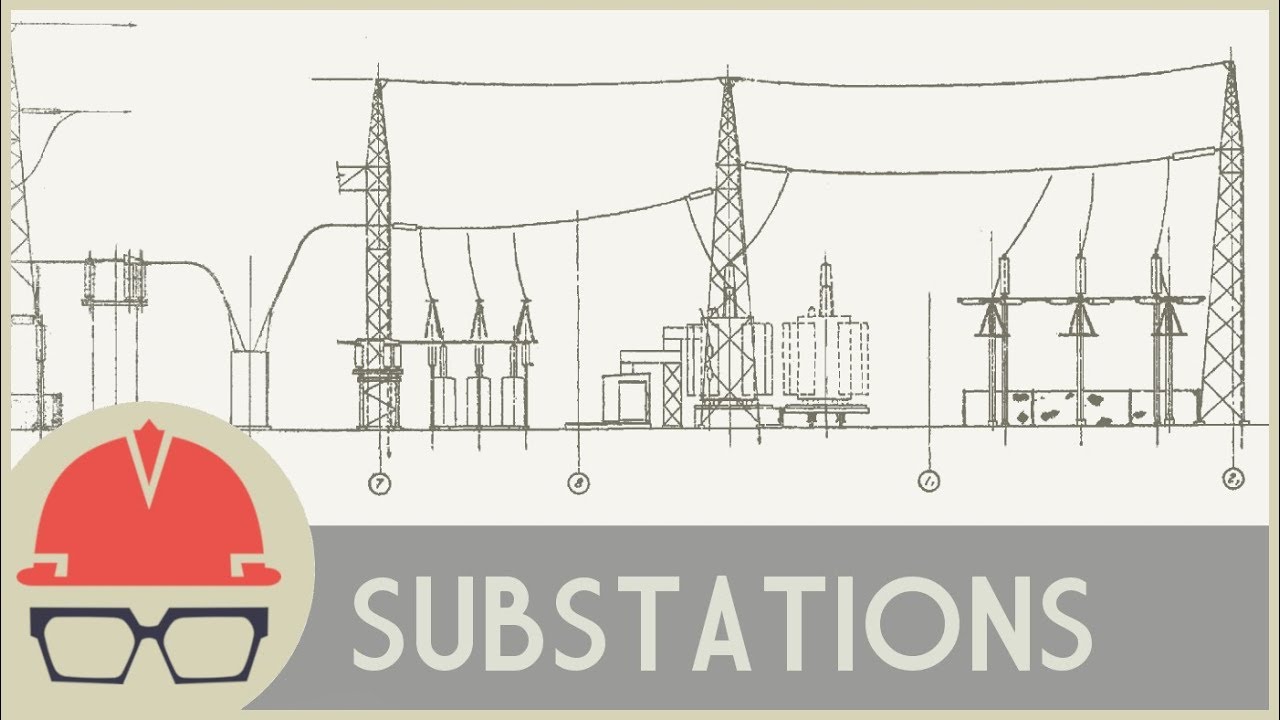
Substations can be designed and constructed for outdoor use, known as air insulated substations (AIS) or for indoor/underground use, known as gas-insulated substations (GIS).

Other items and equipment involved in designing substations which are less expensive than power transformers are: circuit breakers, potential/current transformers, electric bus, steel structures, foundations, control house, protection & controls (P&C), relaying/IEDs, SCADA, control cables, fencing, grounding, real estate, etc. A power utilities’ greatest expense in substations is the power transformer. Power Substations are filled with large and very expensive equipment. A switching station is comprised of various switches and breakers that are used to help control the power flow. Within a switching station, the voltage coming in the station equals the voltage going out. AIS SubstationĪ switching station is different from a substation since it does not have a power transformer and does not transform the voltage supply. Transmission substations take the incoming higher voltage from transmission lines and step them down to a lower voltage for distribution systems, which is in preparation for end user customers. Generating substations step up the voltage from the generator’s lower voltage to a higher voltage which is more economical for transmitting electric power over longer distances with less power losses caused by the impedance of transmission lines. A substation is a station that includes a power transformer for either stepping up or stepping down the supply voltage depending on whether it is a generating substation or transmission/distribution substation. Substations are power stations that include power transformers, potential or voltage transformers, current transformers, electrical bus, breakers, switches, and so on. (See A Basic Explanation Summary of How the Electric Power Grid Works) This is a basic summary and explanation of engineering & design processes used during designing power substations - by Matt Cole, 3 Phase Associates Power Substationsįor the most part, electric power substations are viewed as the most integral part of a power utilities’ electric system, with electric systems being comprised of power generation, transmission, and distribution systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
